
|
genus
|
Ponera
|
 |
Japanese Name
|
Hari-ari-zoku
|
Original Reference
|
|
Latreille, P.A. (1804) Tableau m?thodique des insectes. Classe huiti?me. Insectes, Insecta. Nouveau Dictionnaire d'Histoire Naturelle 24: 129-200.
|
Synonym
|
|
Pseudocryptopone Wheeler, 1933,
Selenopone Wheeler, 1933,
|
Description
|
|
Small to medium-sized ants with yellow to black body color. Eyes small. Mandibles each with 3 or 4 apical teeth followed by a series of small denticles. No small pits on dorsolateral surfaces of mandibular bases. Middle and hind tibiae each with a single pectinate spur. No stout setae on extensor surfaces of middle tibiae. Subpetiolar process with a very characterisatic small anterior light-permeable circular or subcircular "window" (= translucent fenestra) and bilaterally paired small ventral teeth.
|
|
|
Remarks
|
|
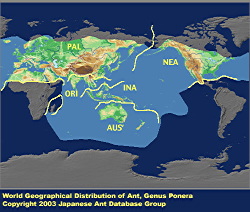
In some cases discrimination from Hypoponera may be difficult, but Ponera is distinguished by its palpal formula being 2:2 and by its larvae (in Japanese species) having three pairs of mushroom-like projections (chalazae) dorsally on the abdomen, versus 4-2 pairs in Hypoponera. Around 30 species have been described, distributed mainly in the Indo-Australian Region. Ponera species nest under stones, in rotting logs, and in the soil. Eight species are known from Japan.
|
References
|
|
- Three obscure genera of ponerine ants. American Museum Novitates 672: 1-23.
- Wilson, E. O., (1957). The tenuis and selenophora groups of the ant genus Ponera. bull. Mus. comp. Zool. Harvard College 116: 355-386.
- Tableau m?thodique des insectes. Classe huiti?me. Insectes, Insecta. Nouveau Dictionnaire d'Histoire Naturelle 24: 129-200.
|
Editor
|
|
Original text by Keiichi Onoyama and Mamoru Terayama. Revised by Masashi Yoshimura. English translation by Keiichi Onoyama, edited by Robert W. Taylor.
|
|