
|
species
|
Amblyopone silvestrii
|
 |
Japanese Name
|
Nokogiri-hari-ari
|
Original Reference
|
|
Wheeler, W.M. (1928) Ants collected by Professor F. Silvestri in Japan and Korea. Bollettino del Laboratorio di Zoologia generale e agraria del R. Istituto Superiore agrario di Portici 22: 96-125.
|
Synonym
|
|
Stigmatomma silvestrii Wheeler, 1928,
Amblyopone silvestrii (Wheeler): Brown, 1960
|
Description
|
|
Total length of workers around 3.5 - 4.5 mm. Body color yellowish brown to reddish brown. The largest Japanese Amblyopone species, distinguished from the rest by its 12-segmented antennae and mandibular dentition, with numerous denticles double-ranked denticles. The frontal lobes cover the antennal insertions and are well separated.
|
Remarks
|
|
A. silvestrii apparently feeds mainly on centipedes (Masuko, 1981). Masuko (1986) discovered the peculiar habit of larval haemolymph feeding, whereby queens wound larvae non-lethally and imbibe their haemolymph as food. Distributed quite widely from near Sapporo in Hokkaido (Onoyama,1989a) to Iriomote Island, but relatively rare.
|
|
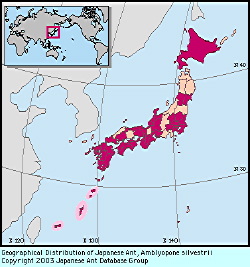
Distribution
|
|
Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu, Tsushima I., Nansei Is; Korean Peninsula, Taiwan.
|
|
References
|
|
- Masuko, K. (1981). Predatory behavior of some forest floor dwelling ants. . Insects and Nature, 16(3), 19-25. .
- Masuko, K. (1986). Larval hemolymph feeding: a nondestructive parental cannibalism in the primitive ant Amblyopone silvestrii Wheeler (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). . Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol., 19, 249-255.
- Onoyama, K. (1989). Three ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) new to Hokkaido, Japan. . Jpn. J. Ent., 57, 604.
|
Editor
|
|
Original text by Keiichi Onoyama. Revised by Masashi Yoshimura. English translation by Keiichi Onoyama, edited by Robert W. Taylor.
|
|